MITIGO™: Making Intrathecal Morphine Sulfate Injections Safer
October 4th, 2022 Drug, Patient, and Provider Safety
Easy-to-use, convenient packaging reduces risks associated with drug administration
There’s more than one option available for prescribing and administering morphine sulfate to chronic pain patients. But, when it comes to safety and ease of use during administration, there is only one option: MITIGO™ (morphine sulfate injection). You know that intrathecal morphine sulfate drug therapy is safer than oral drug therapy, but what separates MITIGO from other ITT options? There are two factors: how MITIGO is packaged and how MITIGO is formulated.
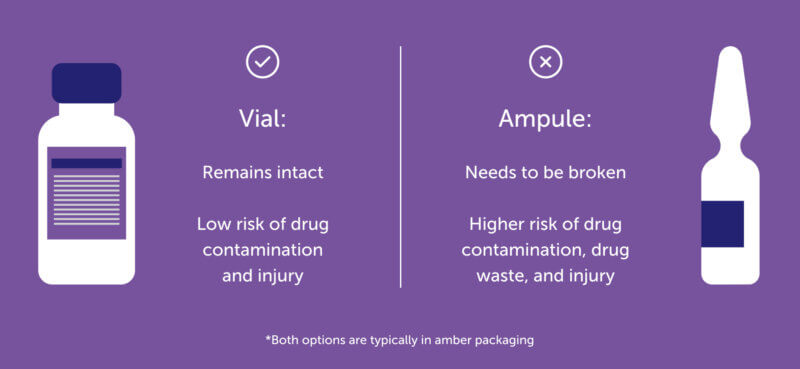
Packaging: Vials vs. Ampules
Would you rather break a glass ampule to get the morphine sulfate prescription ready for injection OR use a ready-to-draw vial that doesn’t require multiple steps to prepare? The answer is obvious. Why risk sharps injury or bacterial contamination due to broken glass? Why risk overdrawing medication and drug waste? Why wait on the pharmacy to mix the drug together when you could be getting it to your patients faster? You don’t have to!
MITIGO is the only FDA-approved injectable morphine packaged in a vial.
It’s easy to interchange the terms vial and ampule but it’s important to remember that they’re two different things. Ampule = glass needs to be broken by hand or via a cracker in order to open and involves multiple steps, vial = no glass breaking and a reduced number of steps enables faster prep.
In addition to the packaging of the drug, which makes it safer for healthcare providers, MITIGO™ (morphine sulfate injection)’s formula maintains its potency, making it more effective for most patients compared to other morphine drug therapies.
Understanding the Non-Compounded Drug Formula
There are two ways that drugs can be formulated – compounded and non-compounded. When you choose MITIGO for chronic pain management, you’re getting a non-compounded drug, which can help the patient experience better relief.
As with vials vs. ampules, non-compounded drugs are easier to administer vs. compounded drugs. Just take it out of the vial and use. There’s no need to mix or dilute the morphine sulfate, which keeps the potency more consistent from dose to dose. Patients will receive the same level of drug strength every time and can count on consistent relief.
MITIGO’s non-compounded formula also results in less drug waste as it has a longer shelf life than compounded drugs and it maintains potency for up to 2 years compared to 24 to 48 hours.
Need more reasons to choose non-compounded morphine sulfate for intrathecal therapy? PACC (Polyanalgesic Consensus Conference) Guidelines recommend only using off-label drug monotherapy or combination therapy, like compounded morphine sulfate, if FDA-approved drugs, like MITIGO, are tried and failed. Additionally, some insurers will not reimburse providers for compounded drugs if another approved drug is available for use.
Choosing MITIGO for Intrathecal Therapy
If you’re ready to experience a safer way to deliver morphine sulfate to your chronic pain patients, contact us to get started with MITIGO (morphine sulfate injection).
Contact us for more information on MITIGO
Important Risk Information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
MITIGO™ (Morphine Sulfate Injection, USP – Preservative-free) is an opioid agonist, for use in continuous microinfusion devices and indicated only for intrathecal or epidural infusion in the management of intractable chronic pain severe enough to require an opioid analgesic and for which alternative treatments are inadequate.
IMPORTANT RISK INFORMATION
WARNING: RISKS WITH NEURAXIAL ADMINISTRATION; LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION; RISK OF ADDICTION, ABUSE, AND MISUSE; NEONATAL OPIOID WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME; and RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Single-dose neuraxial administration may result in acute or delayed respiratory depression up to 24 hours. Because of the risk of severe adverse reactions when MITIGO is administered by the epidural or intrathecal route of administration, patients must be observed in a fully equipped and staffed environment for at least 24 hours after the initial dose.
- Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression may occur. Monitor closely, especially upon initiation or following a dose increase. Patients must be observed in a fully equipped and staffed environment for at least 24 hours after each test dose and, as indicated, for the first several days after surgery.
- MITIGO exposes users to risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death. Assess patient’s risk before prescribing and monitor regularly for these behaviors and conditions.
- Prolonged use of MITIGO during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated. If prolonged opioid use is required in a pregnant woman, advise the patient of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available.
- Concomitant use of opioids with benzodiazepines or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Reserve concomitant prescribing for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate; limit dosages and durations to the minimum required; and follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Significant respiratory depression
- Acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting in absence of resuscitative equipment
- Concurrent use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or use of MAOIs within the last 14 days
- Known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus
- Hypersensitivity or intolerance to morphine
Neuraxial administration of MITIGO is contraindicated in patients with:
- Infection at the injection microinfusion site
- Concomitant anticoagulant therapy
- Uncontrolled bleeding diathesis
- The presence of any other concomitant therapy or medical condition which would render epidural or intrathecal administration of medication especially hazardous.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Risk of Inflammatory Masses: Monitor patients receiving continuous infusion of MITIGO via indwelling intrathecal catheter for new signs or symptoms of neurologic impairment.
- Risk of Tolerance and Myoclonic Activity: Monitor patients for unusual acceleration of neuraxial morphine, which may cause myoclonic-like spasm of lower extremities. Detoxification may be required.
- Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression in Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease or in Elderly, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients: Monitor closely, particularly during initiation and titration.
- Adrenal Insufficiency: If diagnosed, treat with physiologic replacement of corticosteroids, and wean patient off of the opioid.
- Severe Hypotension: Monitor during dosage initiation and titration. Avoid use of MITIGO in patients with circulatory shock.
- Risks of Use in Patients with Increased Intracranial Pressure, Brain Tumors, Head Injury, or Impaired Consciousness: Monitor for sedation and respiratory depression. Avoid use of MITIGO in patients with impaired consciousness or coma.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most serious adverse reactions were respiratory depression, apnea, circulatory depression, respiratory arrest, shock, and cardiac arrest. Other common frequently observed adverse reactions include: sedation, lightheadedness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and constipation.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm.
- Hepatic and Renal Impairment: May affect the metabolism and excretion of MITIGO.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Piramal Critical Care, Inc. at 1-888-822-8431 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
For additional Important Risk Information, including boxed warning, see enclosed Full Prescribing Information.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
MITIGO™ (Morphine Sulfate Injection, USP – Preservative-free) is an opioid agonist, for use in continuous microinfusion devices and indicated only for intrathecal or epidural infusion in the management of intractable chronic pain severe enough to require an opioid analgesic and for which alternative treatments are inadequate.
IMPORTANT RISK INFORMATION
WARNING: RISKS WITH NEURAXIAL ADMINISTRATION; LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION; RISK OF ADDICTION, ABUSE, AND MISUSE; NEONATAL OPIOID WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME; and RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Single-dose neuraxial administration may result in acute or delayed respiratory depression up to 24 hours. Because of the risk of severe adverse reactions when MITIGO is administered by the epidural or intrathecal route of administration, patients must be observed in a fully equipped and staffed environment for at least 24 hours after the initial dose.
- Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression may occur. Monitor closely, especially upon initiation or following a dose increase. Patients must be observed in a fully equipped and staffed environment for at least 24 hours after each test dose and, as indicated, for the first several days after surgery.
- MITIGO exposes users to risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death. Assess patient’s risk before prescribing and monitor regularly for these behaviors and conditions.
- Prolonged use of MITIGO during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated. If prolonged opioid use is required in a pregnant woman, advise the patient of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available.
- Concomitant use of opioids with benzodiazepines or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Reserve concomitant prescribing for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate; limit dosages and durations to the minimum required; and follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Significant respiratory depression
- Acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting in absence of resuscitative equipment
- Concurrent use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or use of MAOIs within the last 14 days
- Known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus
- Hypersensitivity or intolerance to morphine
Neuraxial administration of MITIGO is contraindicated in patients with:
- Infection at the injection microinfusion site
- Concomitant anticoagulant therapy
- Uncontrolled bleeding diathesis
- The presence of any other concomitant therapy or medical condition which would render epidural or intrathecal administration of medication especially hazardous.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Risk of Inflammatory Masses: Monitor patients receiving continuous infusion of MITIGO via indwelling intrathecal catheter for new signs or symptoms of neurologic impairment.
- Risk of Tolerance and Myoclonic Activity: Monitor patients for unusual acceleration of neuraxial morphine, which may cause myoclonic-like spasm of lower extremities. Detoxification may be required.
- Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression in Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease or in Elderly, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients: Monitor closely, particularly during initiation and titration.
- Adrenal Insufficiency: If diagnosed, treat with physiologic replacement of corticosteroids, and wean patient off of the opioid.
- Severe Hypotension: Monitor during dosage initiation and titration. Avoid use of MITIGO in patients with circulatory shock.
- Risks of Use in Patients with Increased Intracranial Pressure, Brain Tumors, Head Injury, or Impaired Consciousness: Monitor for sedation and respiratory depression. Avoid use of MITIGO in patients with impaired consciousness or coma.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most serious adverse reactions were respiratory depression, apnea, circulatory depression, respiratory arrest, shock, and cardiac arrest. Other common frequently observed adverse reactions include: sedation, lightheadedness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and constipation.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm.
- Hepatic and Renal Impairment: May affect the metabolism and excretion of MITIGO.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Piramal Critical Care, Inc. at 1-888-822-8431 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
For additional Important Risk Information, including boxed warning, see enclosed Full Prescribing Information.